Workplace
CEOs Are Hindering LGBTQ+ Equality in the Workplace

This article is republished from The Conversation under a CC BY-ND 4.0 license. Read the original article.
Global acceptance of homosexuality has risen over the past two decades to 72 per cent in 2019 from 51 per cent in 2002. Despite this, a report from last year found that majority of American LGBTQ+ workers have faced job discrimination.
This echoes an earlier report, published by the Canadian Centre for Diversity and Inclusion in 2015, that found many Canadians were uncomfortable disclosing their sexual orientation at work. Just last month, The Canadian Press published an article that found 65 percent of LGBTQ+ employees in Québec have faced discrimination in the past five years.
There is a clear disconnect between the increased tolerance toward LGBTQ+ people in broader society compared to the experience of LGBTQ+ people in the workplace.
As major stakeholders with significant power, corporations have the responsibility to bridge this equality gap and be leaders in making the workplace inclusive and welcoming for their LGBTQ+ employees.
The LGBT Purge
One of the longest, most devastating examples of workplace discrimination in Canada is known as the LGBT Purge. Between the 1950s and mid-1990s, the Canadian government embarked on a purge of LGBTQ+ workers from federal public service and the Canadian Armed Forces.
An estimated 9,000 LGBTQ+ Canadians experienced abuse and violence at the whims of the government that investigated, interrogated and traumatized them.
The LGBT Purge was driven by anticommunist sentiment during the Cold War. Socially stigmatized people, like members of the LGBTQ+ community, were seen as targets for blackmail by the Soviet Union for classified information.
There is no record of any Canadian government employees or members of the Armed Forces turning over evidence to the Soviet Union out of fear their sexual orientation would be exposed.
In 2017, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau apologized for the “state-sponsored, systematic oppression and rejection” of the LGBT Purge. A settlement was reached the following year that included up to $110 million in compensation for survivors of the purge.
The Purge resulted in psychological trauma, material hardship, financial ruin, self-harm and suicide among survivors. The legacy of the Purge, still felt to this day, reminds us that there is still much to be done in the fight for equality.
CEO power and workplace equality
My colleagues and I recently published a research paper investigating if and how chief executive officer’s (CEO) power affects corporate LGBTQ+ equality. To measure corporate LGBTQ+ equality, we used the Corporate Equality Index rating system provided by the Human Rights Campaign.
We decided to study CEO power because CEOs play a key role in investing in corporate LGBTQ+ equality initiatives. They normally set the strategic directions and initiate major decisions in their companies and can influence what initiatives receive funding.
Studies have shown that CEOs improve sustainability because they have higher job security and can focus on long-term initiatives, such as sustainability. A similar argument could be made for LGBTQ+ employee equal rights initiatives. CEOs, who are in the most secure position in their companies, have the ability and flexibility to invest in corporate LGBTQ+ equality.
How power comes into play
Our research found that powerful CEOs discouraged corporate LGBTQ+ equality initiatives. This could be for a number of reasons, including CEOs catering to shareholders who don’t think corporate LGBTQ+ equality initiatives should be invested in, either because it clashes with their beliefs, or they don’t think it’s a worthy investment.
Additionally, we found that powerful CEOs were more likely to discourage corporate LGBTQ+ equality initiatives when corporations lacked external monitoring (lower level of institutional ownership), information transparency (higher tendency to manipulate their earnings) or were headquartered in a state that had a majority religious population.
Surprisingly, CEOs did not suffer any consequences for suppressing LGBTQ+ employee equality initiatives. Instead, some enjoyed better stock market returns and higher long-term firm market values.
But there are greater benefits for investing in LGBTQ+ initiatives. They aren’t just the morally correct thing to do, but can also be good for companies in the long run by improving employee morale, productivity, firm performance and future firm valuation.
It’s time for change
Our findings reinforce previous reports that we have a long way to go in achieving equal rights for LGBTQ+ people, especially in the workplace.
It is clear that corporations will not alter their course unless they are forced to or their bottom line is at stake. It is time for regulators and policy-makers to enact affirmative action regulations to encourage corporations to create equitable and fair workplace environments for their LGBTQ+ employees.
There are a variety of ways this could be accomplished. Activist-investors could motivate their corporations to invest in corporate LGBTQ+ equality initiatives, like they do for environmental causes.
The Canadian Securities Administrators, an umbrella organization of Canada’s provincial and territorial securities regulators, could propose regulations that would require boards of directors to have LGBTQ+ representation, which in turn may influence more LGBTQ+ friendly policies and initiatives by corporations more broadly.
The Conversation is an independent, nonprofit publisher of commentary and analysis, authored by academics and edited by journalists for the general public.
Work
Bisexual employees are less likely to be out at work, but those who are report high levels of discrimination
Cisgender bisexual and gay men often report higher rates of unfair treatment at work compared to lesbian and bisexual women

A new study by the Williams Institute at UCLA School shows that cisgender bisexual employees are less likely to be open about their sexual orientation at work than cisgender gay and lesbian employees. Only about one-third (36%) of cisgender bisexual employees were out to their supervisors, compared to three-quarters (75%) of cisgender gay men and lesbians.
While bisexual employees overall are significantly less likely to report experiencing discrimination and harassment in the workplace than gay and lesbian employees, that difference disappears when looking at the experiences of employees who are open about being LGB at work.
One-quarter (24%) of all cisgender bisexual employees reported experiencing discrimination at work—including being fired or not hired—because of their sexual orientation, compared to 34% of all cisgender gay and lesbian workers. However, when looking at “out” LGB employees, similar proportions of bisexual employees (33%) and gay and lesbian employees (37%) reported experiencing workplace discrimination.
Experiences of discrimination and harassment among out workers differ by gender. Sixty percent of cisgender bisexual men who are out at work experienced verbal, physical, or sexual harassment compared to 38% of out bisexual women and 33% of out lesbians. Out gay men experienced similar levels of harassment as out bisexual men.
Using survey data collected in May 2021 from 935 LGBT adults in the workforce, researchers examined the workplace experiences of cisgender bisexual adults compared to cisgender lesbians and gay men. Workplace experiences of transgender employees were analyzed in a 2021 report.
“The higher rates of concealing their sexual minority identity among bisexual employees may mask the extent to which they experience unfair treatment based on their sexual orientation,” said lead author Christy Mallory, Legal Director at the Williams Institute. “It is vital that policymakers, employers, and researchers take a nuanced approach to understanding and addressing sexual orientation and gender identity discrimination in the workplace to meet the unique needs of these communities.”
Key Findings
Concealing LGB Identity
- One in five (19%) cisgender bisexual employees reported being out to all of their coworkers, compared to half (50%) of cisgender lesbians and gay men.
Discrimination
- Among all cisgender LGB employees, bisexual employees were significantly less likely than gay and lesbian employees to report experiencing discrimination at work including being fired or not hired at some point in their lives (24% v. 34%).
- Among only cisgender LGB employees who were out at work, similar proportions reported experiencing discrimination: 33% of bisexual employees and 37% of gay and lesbian employees reported experiencing workplace discrimination.
- Out gay and bisexual men were more likely to experience employment discrimination than out lesbians and bisexual women: 46% of out bisexual men and 43% of out gay men reported having been fired or not being hired because of their LGB status. In contrast, about one-quarter of out lesbians (25%) and out bisexual women (27%) reported similar experiences.
Harassment
- Among all cisgender LGB employees, 34% of bisexual employees and 42% of gay and lesbian employees reported experiencing at least one type of harassment (verbal, physical, or sexual) in the workplace at some point in their lives.
- Among only cisgender LGB employees who were out at work, 60% of out bisexual men reported one form of harassment (verbal, physical, or sexual), compared to 38% of bisexual women and 33% of out lesbians.
Retention
- Among only cisgender LGB employees who were out at work, 58% of bisexual men and 50% of gay men said they had left a job because of unfair treatment compared to 35% of lesbians and 29% of bisexual women.
Work
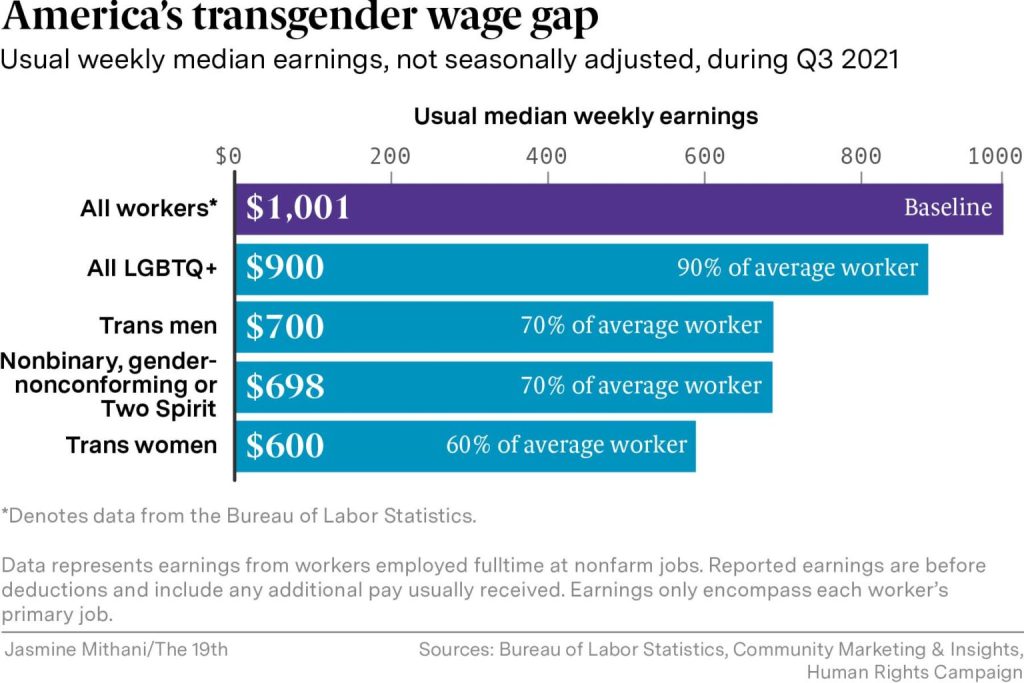
Full-time trans workers face a wage gap, poll finds
Trans and gender-nonconforming people are among the lowest paid LGBTQ+ full-time workers in the United States, a new snapshot poll shows.

This story was originally published by The 19th
 Transgender and gender-nonconforming people are among the lowest paid LGBTQ+ people working full time in the United States, according to a snapshot poll by the Human Rights Campaign Foundation and a California-based market research firm.
Transgender and gender-nonconforming people are among the lowest paid LGBTQ+ people working full time in the United States, according to a snapshot poll by the Human Rights Campaign Foundation and a California-based market research firm.
The HRC found that trans men and nonbinary or gender-nonconforming people earn 70 cents for every dollar the typical worker earns, while trans women earn 60 cents to that dollar, based on responses from roughly 6,800 LGBTQ+ workers last spring.
“If that’s across the entire population, those dollars and cents add up,” said Spencer Watson, executive director at the Center for LGBTQ Economic Advancement & Research.
The HRC believes the actual pay gap for trans and LGBTQ+ people is bigger because part-time jobs and work in underground economies were not considered. But the survey still offers a unique look at wage disparities that experts say have not been adequately researched.
Trans people experience widespread unemployment and poverty at higher rates compared to the rest of the U.S. population. Even if a trans person does get a job outside of the underground economy, discrimination can still take its toll and stunt economic advancement, said Josie Caballero, survey project manager of the U.S. Transgender Survey (USTS).
More than 77 percent of respondents to the 2015 USTS — the most comprehensive survey of trans life and the latest data available ahead of the survey’s planned 2022 release — described taking multiple steps to avoid discrimination at work, like hiding their gender identity, delaying their transition and being misgendered without correcting their employer.
“If you’re just trying to avoid discrimination, you’re not you’re not asking for promotions,” Caballero said. “You’re not trying to seek quality of life. You’re just trying to survive and keep your head down.”
The wage gaps, Caballero said, “kind of confirm what we already know.”
As researchers investigate the economic disparities faced by trans people, they should be focused on what kind of wage gap trans women of color experience in the United States, said Lourdes Ashley Hunter, executive director of the Trans Women of Color Collective. Researchers also need to account for underground economies and sex work in order to gain a full picture of the economic disparities that most sharply harm trans women of color, who also face disproportionate violence and multiple forms of discrimination, Hunter said.
In the formal economy, how a company is structured to support Black trans women and other women of color is also key to their economic opportunities, Hunter said. Are managers hiring only one or a few trans people? Are there trans people of color in leadership? Is the company paying a living wage? And even if a Black trans person is making a living wage — how long were they in poverty before that?
The HRC’s polling analyzed the reported wages of LGBTQ+ women of color, though a wage gap for trans men and trans women of color was not measured due to a lack of data. The organization hopes to release another report focused on Black and Latinx trans people from the same data used in this report, Shoshana Goldberg, the organization’s director of public education and research, said.
“We’re only just now being able to start to uncover a lot of these economic disparities,” she said.
Although trans women in HRC’s poll were the lowest paid of any group, cisgender queer women who responded to the survey also shared gaps in pay. However, data from the UCLA’s Williams Institute indicates a more complicated financial picture for cisgender bisexual and lesbian women. Cisgender lesbian and bisexual women face significant discrimination and economic stress, and queer women of color are significantly more likely to have very low household incomes compared to White women, according to the Williams Institute at the UCLA School of Law.
But, comparing cisgender queer women’s wages to straight women’s wages is more complicated, said M.V. Lee Badgett, economics professor and distinguished scholar at the Williams Institute.
Cisgender lesbian and bisexual women on average make more money than straight women, Badgett said, for a variety of reasons, including working more hours and working more weeks of the year — which can be influenced by relationship structure and a lack of child care. However, they make less on average than bisexual and gay cisgender men, she added. Recent data from the Hamilton Project also found that married women couples tend to bring home lower wages than an opposite-gender married couple.
Sixteen percent of trans people surveyed by USTS were either making less than $10,000 per year in 2014 or had no income. As the census’ Household Pulse Survey gathers information on how Americans are faring during the pandemic — recently including LGBTQ+ people in the count — researchers are learning that trans people are currently still more likely to have household incomes that put them below the federal poverty line, said Kitt Carpenter, labor economist and founder of the Vanderbilt LGBT Policy Lab.
Investigating a potential trans wage gap presents a new area for researchers to articulate the day-to-day economic disparities of trans people, in line with discussions on the racial wage gap and gender wage gap in the United States, Watson said.
And at the end of the day, researchers are “only beginning to scratch the surface” of the experiences of trans people and other gender minorities, and that understanding is much further behind research on LGBTQ+ people as a whole, Carpenter said.
“But thankfully, we’re moving in the right direction,” he said.
The 19th is an independent, nonprofit newsroom reporting at the intersection of gender, politics and policy.
Workplace
One in ten LGBT workers experienced discrimination at work in the last year
LGBT employees of color were more likely to report being denied jobs and verbal harassment.

A new study by the Williams Institute at UCLA School of Law finds an estimated 46% of LGBT workers have experienced unfair treatment at work at some point in their lives, including being fired, not hired, or harassed because of their sexual orientation or gender identity.
An estimated 9% of LGBT employees reported experiences of discrimination in the past year, despite the U.S. Supreme Court’s 2020 decision in Bostock v. Clayton County, which extended employment non-discrimination protections to LGBT people nationwide. Approximately 11% of LGBT employees of color reported being fired or not hired because of their sexual orientation or gender identity in the last year.
Using survey data collected in May 2021 from 935 LGBT adults in the workforce, researchers examined lifetime, five-year, and past-year discrimination among LGBT employees.
Results show that over half (57%) of LGBT employees who experienced discrimination or harassment at work reported that the unfair treatment was motivated by religious beliefs, including 64% of LGBT employees of color and 49% of white LGBT employees.
“Employment discrimination and harassment against LGBT people remain persistent and pervasive in 2021,” said lead author Brad Sears, Founding Executive Director at the Williams Institute. “Passing the Equality Act would ensure that LGBT people—particularly transgender people and LGBT people of color—are allowed to participate fully in the workplace as well as other public settings.”
Additional Findings
Discrimination
- 30% of LGBT employees reported experiencing at least one form of employment discrimination (being fired or not hired) because of their sexual orientation or gender identity at some point in their lives.
- 29% of LGBT employees of color reported not being hired compared to 18% of white LGBT employees.
Harassment
- 38% of LGBT employees reported experiencing at least one form of harassment (including verbal, physical, or sexual harassment) at work because of their sexual orientation or gender identity at some point in their lives.
- LGBT employees of color were significantly more likely to experience verbal harassment than white and cisgender employees.
- 36% of LGBT employees of color reported experiencing verbal harassment compared to 26% of white LGBT employees.
Religious Motivation
- Of employees who experienced discrimination or harassment at some point in their lives, 64% of LGBT employees of color said that religion was a motivating factor compared to 49% of white LGBT employees.
Avoiding Discrimination
- Half (50%) of LGBT employees said that they are not open about being LGBT to their current supervisor and one-quarter (26%) are not out to any of their co-workers.
- Many LGBT employees reported engaging in “covering” behaviors to avoid harassment or discrimination at work, such as changing their physical appearance and avoiding talking about their families or social lives at work.
- For example, 36% of transgender employees said that they changed their physical appearance and 28% said they changed their bathroom use at work to avoid discrimination and harassment.